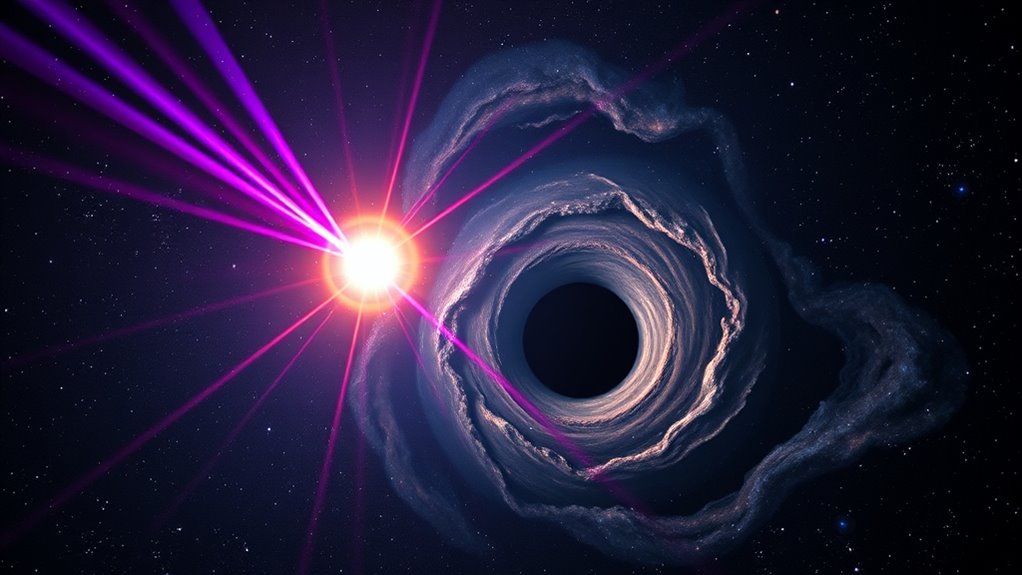
Recent advances in multi-messenger astronomy let you observe neutron star and black hole collisions through both gravitational waves and electromagnetic signals. These events reveal extreme physics, helping you understand how dense objects form and evolve. By combining different data types, scientists pinpoint locations more accurately and uncover phenomena like heavy element creation. If you keep exploring, you’ll discover how these breakthroughs are transforming our view of the universe’s most energetic interactions.
Key Takeaways
- Multi-messenger astronomy combines gravitational wave and electromagnetic observations to study neutron star and black hole collisions comprehensively.
- Recent advances enable precise localization of cosmic collisions, enhancing understanding of their physical processes.
- Gravitational wave detection reveals object masses and spins, confirming theories of dense object formation.
- Electromagnetic signals like gamma-ray bursts provide insights into matter physics during mergers.
- Future detector improvements will increase collision observations, deepening knowledge of extreme cosmic phenomena.

When neutron stars and black holes collide, some of the universe’s most energetic and mysterious events unfold. These cosmic encounters release enormous amounts of energy, producing gravitational waves, light, and other signals that travel across space. As a result, astronomers have a rare opportunity to observe phenomena that challenge our understanding of physics and the universe’s most extreme objects. You can imagine how exciting it is to be part of this frontier, where cutting-edge technology helps uncover secrets hidden deep within these violent mergers.
These events are incredibly complex, involving the interplay of gravity, matter, and radiation under conditions that can’t be replicated on Earth. When a neutron star, a dense remnant of a massive star’s core, collides with a black hole, the intense gravitational pull of the black hole often tears apart the neutron star before it crosses the event horizon. This process emits a burst of gravitational waves—ripples in spacetime—that detectors on Earth can pick up. You might think of these waves as cosmic fingerprints, uniquely identifying each collision and helping scientists measure the masses and spins of these objects. This information is essential because it confirms theories about how black holes and neutron stars form and evolve.
Neutron stars torn apart by black holes emit gravitational waves, revealing their properties and confirming theories of cosmic evolution.
In addition to gravitational signals, these collisions can produce electromagnetic emissions, such as gamma-ray bursts, X-rays, and visible light. These signals travel through space and can be detected by telescopes across different wavelengths. When you combine gravitational wave data with electromagnetic observations, you’re tapping into multi-messenger astronomy—a revolutionary approach that offers a more complete picture of these violent events. This synergy allows scientists to pinpoint locations in the universe, understand the physics of extreme matter, and even refine measurements of the universe’s expansion rate.
The advances in multi-messenger astronomy mean that you, as an observer, get a richer, more detailed understanding of cosmic collisions than ever before. Instead of relying solely on a single type of signal, researchers now analyze combined data to interpret what’s happening during these cataclysmic events. It’s akin to watching a complex play from multiple angles simultaneously, revealing nuances that would otherwise remain hidden. This integrated approach has already led to groundbreaking discoveries, such as confirming that neutron star mergers produce heavy elements like gold and platinum, and providing new constraints on the nature of gravity under extreme conditions.
As detectors improve and more collisions are observed, you can expect a rapid expansion in our knowledge. Each detection not only confirms existing theories but also raises new questions, pushing the boundaries of what we know about the universe’s most energetic phenomena.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Neutron Star-Black Hole Mergers Influence Galaxy Evolution?
Neutron star-black hole mergers shape galaxy evolution by releasing massive energy, generating heavy elements, and triggering star formation. When these collisions occur, you see bursts of gravitational waves and electromagnetic signals that influence surrounding gas and dust. This process enriches the galaxy with new elements, fueling future stars. As a result, these mergers help drive the growth and chemical complexity of galaxies, impacting their long-term development and structure.
Can These Collisions Help Identify Dark Matter Properties?
Imagine trying to find a needle in a cosmic haystack—that’s what identifying dark matter feels like. Collisions between neutron stars and black holes generate signals that help scientists understand extreme gravity and matter under intense conditions, indirectly revealing dark matter’s properties. These events act like cosmic clues, guiding you toward understanding dark matter’s elusive nature by providing data that can’t be obtained through other means.
What Role Do Gravitational Waves Play in Detecting Distant Events?
Gravitational waves help you detect distant cosmic events by passing through space and reaching Earth, carrying information about massive objects like black holes and neutron stars. When these waves arrive, you can analyze their signals to locate and understand the origins of collisions that are otherwise invisible. They act as messengers, revealing details about events billions of light-years away, expanding your understanding of the universe’s most extreme phenomena.
How Might These Events Affect Surrounding Planetary Systems?
These cosmic events can gently disturb nearby planetary systems, causing subtle shifts in orbits or sparking energetic bursts of radiation. You might notice increased radiation exposure or slight orbital variations, but overall, these effects tend to be minimal for distant systems. While they may influence the environment, they rarely cause catastrophic changes, offering a fascinating glimpse into the universe’s delicate balance and the resilience of celestial bodies.
Are There Potential Signals Indicating the Formation of New Elements?
Yes, you can detect signals indicating the formation of new elements during neutron star and black hole collisions. These events produce intense gamma-ray emissions and gravitational waves that carry signatures of heavy elements forming through rapid neutron capture. By analyzing these signals with advanced telescopes and detectors, you can identify the presence of newly synthesized elements, confirming that these cosmic collisions contribute considerably to the universe’s chemical enrichment.
Conclusion
As you explore neutron star and black hole collisions, you witness the universe’s extremes—intense gravity and delicate signals. These violent events contrast with the gentle ripples they send across spacetime, revealing secrets of matter and gravity. By combining messengers, you bridge the immense and the minute, transforming cosmic chaos into understanding. In this dance of destruction and discovery, you realize that even in destruction, the universe offers profound insights waiting to be uncovered.