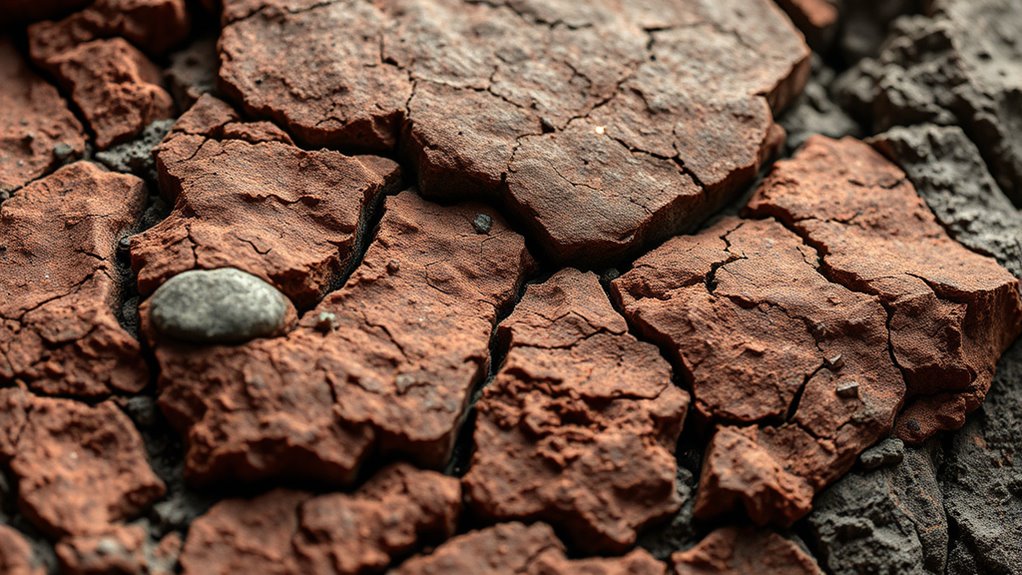
Proto-Earth remnants, like ancient mantle rocks, are invaluable clues to understanding our planet’s earliest origins. They offer direct insights into Earth’s infancy, revealing clues about formation, differentiation, and early mantle composition. These rocks help you grasp how Earth evolved from a molten body to its current state. Exploring these natural archives uncovers the story of our planet’s deep history. Keep exploring to discover more about how these rare remnants shape our understanding of Earth’s profound past.
Key Takeaways
- Mantle remnants preserve chemical signatures of Earth’s early formation, offering clues about the planet’s primordial state.
- These ancient rocks originate from depths exceeding 660 km, providing direct insights into Earth’s deep interior.
- Studying mantle rocks reveals processes of planetary differentiation, including core formation and mantle composition.
- Isotopic and mineral analyses help reconstruct Earth’s early geological history and mantle evolution.
- Mantle remnants serve as natural archives, unlocking secrets of Earth’s infancy and planetary formation processes.
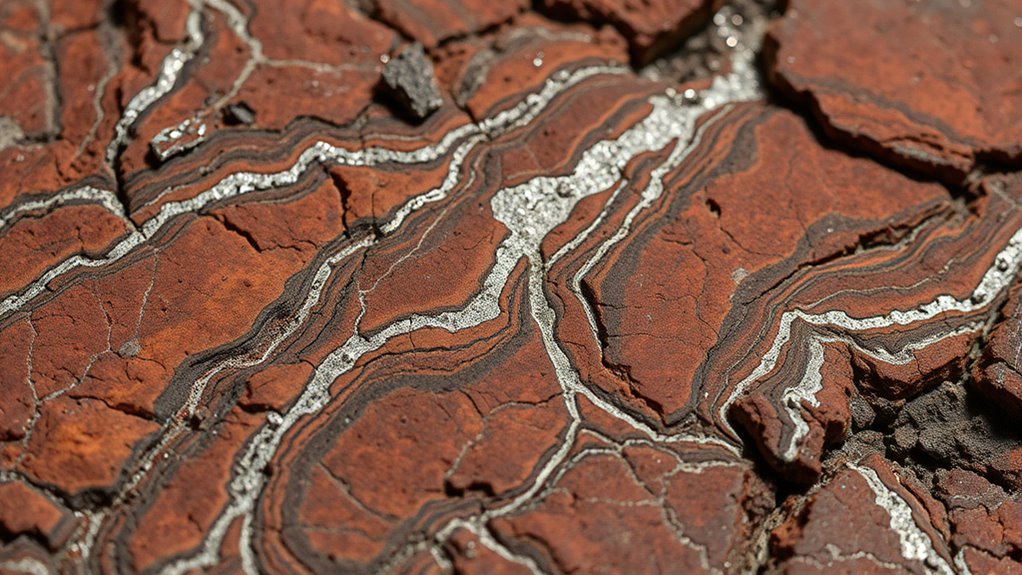

Have you ever wondered what remains of Earth’s earliest form? Deep beneath your feet, ancient rocks hold clues to the planet’s infancy, remnants of a time when Earth was still taking shape. These remnants, primarily found within the mantle, are like pages from a prehistoric diary, telling stories of cosmic collisions, melting, and differentiation that created the world we live on today. They’re not easy to find or study; instead, scientists rely on rare mantle-derived rocks and mineral inclusions that have survived countless geological processes. Through these remnants, we gain insight into the conditions that prevailed over four billion years ago, revealing how Earth evolved from a molten mass into a solid planet with a layered structure. Studying these mantle rocks also helps scientists understand the planetary differentiation process, which shaped the internal structure of Earth. When you look at mantle rocks, you’re peering into a deep history that predates the crust we walk on. These rocks, often brought to the surface via volcanic activity, originate from depths exceeding 660 kilometers, where extreme heat and pressure shape their composition. They’re like snapshots frozen in time, preserving the chemical signatures and mineral structures that tell us about the composition of Earth’s early mantle. These clues help scientists understand the differentiation process—how dense materials sank inward to form the core, while lighter elements rose to create the mantle and crust. Each piece of mantle rock is a puzzle piece, offering insights into the early Earth’s dynamic environment, including the early formation of continents, oceans, and the atmosphere. The significance of these mantle remnants extends beyond just understanding Earth’s early history. They also reveal how the planet’s interior has evolved over billions of years, influenced by processes like mantle convection, volcanic activity, and tectonic shifts. As you consider these rocks, think of them as messengers from a distant past, carrying information about the Earth’s primordial state. Studying their isotopic compositions, mineral inclusions, and chemical signatures allows scientists to reconstruct the timeline of planetary differentiation and the initial building blocks of Earth’s crust. These findings contribute to a broader understanding of planetary formation, not only on Earth but also for other rocky planets in our solar system. In essence, Earth’s early mantle remnants are invaluable. They serve as natural archives, offering a direct link to the planet’s origins. By examining them, you participate in a scientific quest to understand how Earth transformed from a chaotic, molten sphere into the complex, life-supporting world it is today. Each discovery enriches our knowledge of planetary evolution, helping us appreciate the incredible journey our planet has undergone over billions of years.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Mantle Rocks Survive Millions of Years Underground?
Mantle rocks survive millions of years underground because they’re deeply buried, where high pressure and temperature conditions keep them stable. You might think they’d break down, but the intense pressure prevents melting and erosion. Additionally, tectonic plates move slowly, preserving these rocks in stable environments. Their mineral composition also resists weathering, allowing them to remain intact for eons, revealing Earth’s ancient history to you through their preserved structures.
Can Mantle Remnants Be Found on Earth’s Surface Today?
Yes, you can find mantle remnants on Earth’s surface today. These rocks, called xenoliths, are brought up by volcanic eruptions, especially in certain types of volcanoes like kimberlites. When you examine these rocks, you’re seeing pieces of the mantle that have traveled upward through the crust. Scientists study them to learn about Earth’s deep interior, giving you valuable insights into our planet’s origins and composition.
What Techniques Are Used to Analyze Ancient Mantle Rocks?
Like detectives deciphering a hidden code, you use techniques such as electron microprobe analysis, which examines mineral compositions at microscopic levels, and isotopic analysis, revealing age and origin through isotope ratios. Additionally, you utilize seismic tomography to image deep structures and X-ray diffraction to identify mineral phases. Together, these methods uncover the secrets of ancient mantle rocks, helping you understand Earth’s formative years with remarkable precision.
How Do Mantle Remnants Inform Us About Earth’s Early Atmosphere?
You learn about Earth’s early atmosphere by studying mantle remnants because they contain minerals and isotopes that record past conditions. When you analyze these rocks, you can identify gases trapped within them or trace element signatures that reveal the composition of the atmosphere at the time of formation. This helps you understand how Earth’s atmosphere evolved, including the rise of oxygen and other key atmospheric changes over billions of years.
Are There Specific Locations Known for Containing These Ancient Mantle Rocks?
You can find ancient mantle rocks primarily in regions like the Kaapvaal Craton in South Africa and the Siberian Traps in Russia. These areas have exposed deep mantle materials due to tectonic activity and volcanic processes. Exploring these locations allows you to study preserved mantle remnants, providing insights into Earth’s early formation and evolution. Visiting these sites offers a unique glimpse into our planet’s ancient interior.
Conclusion
These ancient mantle rocks are like echoes of Earth’s first heartbeat, whispering stories of our planet’s birth. By studying them, you glimpse the primordial forge where continents and oceans took shape, revealing a world constantly reborn from cosmic chaos. Just as a master sculptor carves beauty from raw stone, these remnants sculpt your understanding of our origins, reminding you that beneath today’s surface lies a deep history — a silent symphony of Earth’s ancient soul waiting to be heard.